C++標準庫中的頭文件是一個功能強大且廣泛使用的工具包,提供了各種常見的算法函數,幫助開發者高效地處理數據。
algorithm.h頭文件是C++標準庫的一部分,它提供了大量的算法模板,可以用于解決各種復雜的計算問題。這些算法包括排序、搜索、合并、轉換等,它們可以幫助我們更高效地處理數據,提高程序的性能。

std::sort 用于對范圍內的元素進行排序。
#include <algorithm>#include <vector>#include <iostream>int main() { std::vector<int> vec = {4, 2, 5, 1, 3}; std::sort(vec.begin(), vec.end()); for (int n : vec) { std::cout << n << " "; } return 0;}
std::reverse 用于反轉范圍內的元素順序。
#include <algorithm>#include <vector>#include <iostream>int main() { std::vector<int> vec = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; std::reverse(vec.begin(), vec.end()); for (int n : vec) { std::cout << n << " "; } return 0;}
std::find 在范圍內查找第一個等于給定值的元素。
#include <algorithm>#include <vector>#include <iostream>int main() { std::vector<int> vec = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; auto it = std::find(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 3); if (it != vec.end()) { std::cout << "Element found: " << *it << std::endl; } else { std::cout << "Element not found" << std::endl; } return 0;}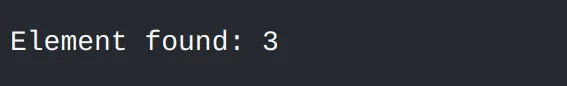
std::accumulate 用于計算范圍內元素的累積和(需要頭文件)。
#include <numeric>#include <vector>#include <iostream>int main() { std::vector<int> vec = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; int sum = std::accumulate(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 0); std::cout << "Sum: " << sum << std::endl; return 0;}
std::count 用于計算范圍內等于給定值的元素個數。
#include <algorithm>#include <vector>#include <iostream>int main() { std::vector<int> vec = {1, 2, 3, 1, 1, 4, 5}; int count = std::count(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 1); std::cout << "Count of 1s: " << count << std::endl; return 0;}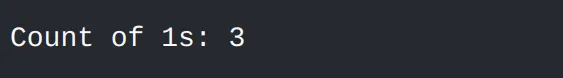
std::copy 將范圍內的元素復制到另一范圍。
#include <algorithm>#include <vector>#include <iostream>int main() { std::vector<int> vec1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; std::vector<int> vec2(5); std::copy(vec1.begin(), vec1.end(), vec2.begin()); for (int n : vec2) { std::cout << n << " "; } return 0;}
std::remove 移除范圍內等于給定值的元素,但不改變容器大小。
#include <algorithm>#include <vector>#include <iostream>int main() { std::vector<int> vec = {1, 2, 3, 1, 4, 1, 5}; auto new_end = std::remove(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 1); vec.erase(new_end, vec.end()); // 可選:刪除多余元素 for (int n : vec) { std::cout << n << " "; } return 0;}
std::unique 用于移除連續的重復元素。
#include <algorithm>#include <vector>#include <iostream>int main() { std::vector<int> vec = {1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5}; auto new_end = std::unique(vec.begin(), vec.end()); vec.erase(new_end, vec.end()); // 可選:刪除多余元素 for (int n : vec) { std::cout << n << " "; } return 0;}
std::lower_bound 在已排序范圍內查找首個不小于給定值的元素。
#include <algorithm>#include <vector>#include <iostream>int main() { std::vector<int> vec = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; auto it = std::lower_bound(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 3); if (it != vec.end()) { std::cout << "Lower bound: " << *it << std::endl; } else { std::cout << "Element not found" << std::endl; } return 0;}
std::upper_bound 在已排序范圍內查找首個大于給定值的元素。
#include <algorithm>#include <vector>#include <iostream>int main() { std::vector<int> vec = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; auto it = std::upper_bound(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 3); if (it != vec.end()) { std::cout << "Upper bound: " << *it << std::endl; } else { std::cout << "Element not found" << std::endl; } return 0;}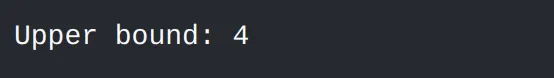
std::equal_range 在已排序范圍內查找等于給定值的子范圍。
#include <algorithm>#include <vector>#include <iostream>int main() { std::vector<int> vec = {1, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 5}; auto range = std::equal_range(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 3); std::cout << "Range of 3s: "; for (auto it = range.first; it != range.second; ++it) { std::cout << *it << " "; } return 0;}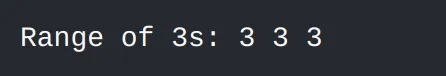
std::merge 將兩個已排序范圍合并為一個有序范圍。
#include <algorithm>#include <vector>#include <iostream>int main() { std::vector<int> vec1 = {1, 3, 5}; std::vector<int> vec2 = {2, 4, 6}; std::vector<int> result(6); std::merge(vec1.begin(), vec1.end(), vec2.begin(), vec2.end(), result.begin()); for (int n : result) { std::cout << n << " "; } return 0;}
std::transform 對范圍內的元素應用給定的函數,并將結果存儲到另一范圍。
#include <algorithm>#include <vector>#include <iostream>int main() { std::vector<int> vec = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; std::vector<int> result(5); std::transform(vec.begin(), vec.end(), result.begin(), [](int x) { return x * x; }); for (int n : result) { std::cout << n << " "; } return 0;}
以上介紹了頭文件中的十三種常見算法,并通過代碼示例展示了它們的使用方法。這些算法極大地簡化了數據處理任務,使代碼更簡潔、更高效。
本文鏈接:http://www.www897cc.com/showinfo-26-88920-0.htmlC++ algorithm.h 頭文件的常見算法的使用
聲明:本網頁內容旨在傳播知識,若有侵權等問題請及時與本網聯系,我們將在第一時間刪除處理。郵件:2376512515@qq.com
上一篇: 微服務如何灰度發布?你會嗎?